Cellophane is often described as biodegradable, but the reality is more complex.
True cellophane is made from regenerated cellulose and can biodegrade under certain conditions, however many products sold today as “cellophane bags” are not genuine cellophane at all.
This distinction matters for brands, packaging buyers, and compliance teams, as misleading eco claims can create regulatory and greenwashing risks.

What Is Cellophane Made Of?
Cellophane is a cellulose-based film originally developed from wood pulp or cotton linters.
It is classified as a regenerated cellulose material, meaning it is derived from natural plant fibers rather than petroleum.
However, in modern packaging markets, the term “cellophane” is frequently misused.
Many so-called cellophane bags are actually made from:
- OPP (Oriented Polypropylene)
- BOPP films
- Other petroleum-based plastics
These materials are not biodegradable, despite being marketed under the cellophane name.
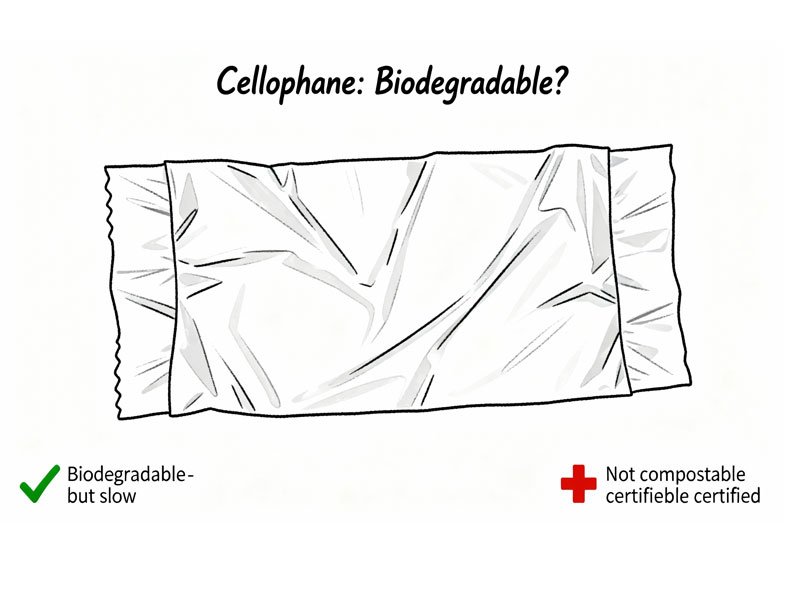
Is Cellophane Biodegradable or Compostable?
Is cellophane biodegradable?
Yes, authentic cellulose cellophane can biodegrade, as microorganisms are able to break down cellulose over time.
However:
- The biodegradation rate is slow and unpredictable
- Decomposition depends heavily on moisture, temperature, oxygen, and microbial activity
- Biodegradable does not mean environmentally safe in all disposal scenarios
Is cellophane compostable?
In most cases, cellophane is not considered certified compostable.
Certified compostable materials must meet standards such as:
- ASTM D6400 (USA)
- EN 13432 (Europe)
- OK Compost (TÜV Austria)
Traditional cellophane generally does not meet these standards, meaning it cannot be reliably processed in industrial composting facilities.
How Long Does Cellophane Take to Decompose?
There is no single answer.
- In controlled laboratory or soil conditions, cellulose films may degrade over months
- In real-world environments (landfill, dry soil, marine settings), degradation can take years
- Surface coatings and additives further slow the process
This uncertainty is why many regulators and composting facilities do not accept cellophane as compostable packaging.
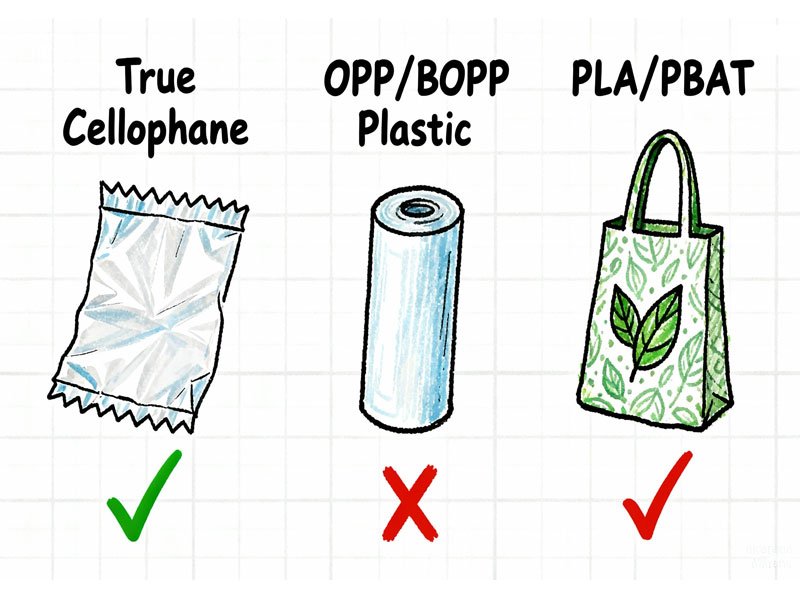
Cellophane vs Plastic vs Certified Compostable Materials
| Material | Biodegradable | Compostable | Certification |
|---|---|---|---|
| True Cellophane (Cellulose) | Yes (slow) | No (typically) | None |
| OPP / BOPP (“Fake cellophane”) | No | No | None |
| PLA / PBAT Blends | Yes | Yes | ASTM D6400 / EN 13432 |
This comparison highlights why certified compostable packaging materials are increasingly preferred over cellophane in regulated markets.
Regulatory & Greenwashing Risks for Brands
From a B2B perspective, the biggest issue with cellophane is mislabeling risk.
Common risks include:
- Marketing plastic films as “cellophane” or “eco-friendly”
- Using biodegradable claims without certification
- Non-compliance with plastic bans or EPR regulations
Regulators and retailers increasingly require clear, verifiable compostable certifications, not ambiguous material descriptions.
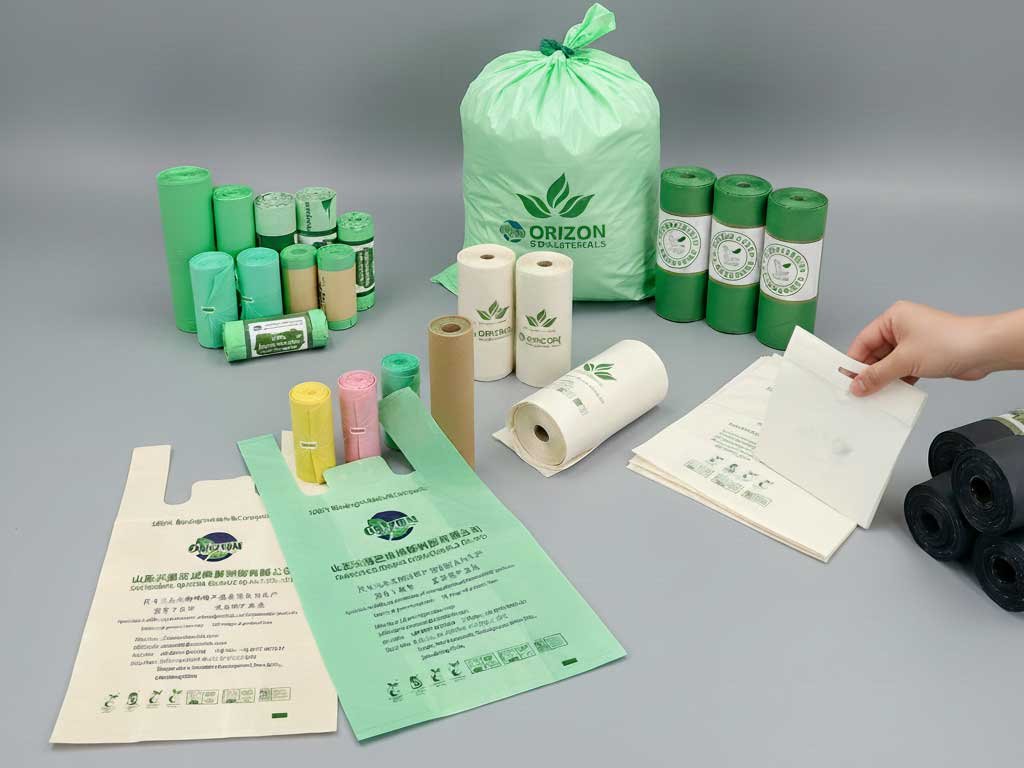

Better Compostable Alternatives to Cellophane Packaging
Brands seeking sustainable packaging are gradually moving away from cellophane toward certified compostable alternatives, such as:
- PLA / PBAT compostable films
- Compostable shopping bags
- Compostable apparel and garment packaging
- Compostable garbage and food waste bags
These materials offer:
- Predictable degradation
- Regulatory acceptance
- Reduced greenwashing risk
Compostable Packaging Solutions for Brands
For brands and distributors, selecting packaging materials should focus on certification, performance, and compliance, rather than marketing terminology.
Certified compostable packaging solutions are widely used in:
- Retail shopping bags
- Apparel and garment packaging
- Waste and sanitation applications
👉 Explore certified compostable apparel packing bag solutions for wholesale and OEM supply
FAQ
Is cellophane eco-friendly?
Cellophane is plant-based, but eco-friendliness depends on disposal conditions and certification. It is not universally compostable.
Is cellophane plastic-free?
True cellophane is plastic-free, but many products marketed as cellophane are actually plastic films.
Can cellophane be home composted?
Generally no. Most cellophane products are not certified for home composting.
Is cellophane allowed under plastic bans?
In many regions, cellophane does not qualify as a certified compostable alternative and may still be restricted.
Conclusion
So, is cellophane biodegradable? Yes, under specific conditions — but biodegradable does not equal compostable, compliant, or low-risk.
For brands and packaging buyers, relying on certified compostable materials rather than ambiguous material names is the safest and most sustainable approach.




