How Importers Check Compostable Bag Quality
Importers should check compostable bag quality by verifying third-party certifications (BPI, EN 13432, ASTM D6400), confirming PLA/PBAT material composition without PE, reviewing recent lab test reports, and performing basic strength and leak-proof tests on samples. Reliable suppliers provide verifiable certificate numbers, traceable materials, and consistent quality control.
Importer Pre-Order Checklist
- Verify certificate numbers on official databases (BPI, DIN CERTCO, TÜV).
- Request recent lab test reports (biodegradation, heavy metals, ecotoxicity).
- Inspect random samples for thickness uniformity, seam strength, and leakage.
- Confirm export experience to regulated markets (US, EU, Australia).
As global regulations on plastic waste become stricter, compostable bags are increasingly used in retail, pet waste, food service, and municipal waste collection. However, not all products labeled “compostable” meet international standards.
For importers, distributors, and brand owners, low-quality or fake compostable bags can lead to customs rejection, regulatory penalties, customer complaints, and long-term brand damage.
As a manufacturer with 16 years of experience biodegradable compostable bags manufacturing , our products comply with BPI and ASTM D6400 certifications. This article will detail how to identify compostable bags, including demonstration videos to help you assess a bag’s strength and leak-proofness. It also includes information on how to verify that a bag is made from plant-based materials like cornstarch, and the misconception that BPI certification isn’t simply a “buy-and-go” option. With this knowledge, you can avoid low-quality products and ensure you choose bags that are truly environmentally friendly and durable.

How to Verify Compostable Bag Certifications (BPI, EN 13432, ASTM D6400)
The first and most important step in checking compostable bag quality is certification verification.
High-quality compostable bags must be certified by recognized third-party organizations. Common international standards include:
- ASTM D6400 (North America) – Verified through the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI)
- EN 13432 (European Union) – Certified by TÜV Austria or DIN CERTCO
- AS 4736 / AS 5810 (Australia) – Industrial and home composting standards
- OK Compost (Industrial / Home) – TÜV Austria certification
Certification is not a logo that can be purchased. It requires laboratory testing for biodegradability, disintegration, heavy metals, and ecotoxicity.
Buyers should always:
- Request the certificate number
- Verify it on the official certification database
- Reject products labeled “certification in progress” without documentation
If a supplier cannot provide a verifiable certificate number, the product should be treated as high risk.

What Materials Should High-Quality Compostable Bags Be Made Of?
Compostable bags differ from typical biodegradable bags or traditional plastic bags. Truly compostable bags completely decompose into water, carbon dioxide, and organic matter under specific conditions (such as industrial or home composting), without releasing microplastics. They are typically made from plant-based materials, such as polylactic acid (PLA), derived from corn starch or other renewable resources.
- Material Composition: Materials such as PLA and PBAT (a compostable copolymer) provide sufficient strength and flexibility.
- Benefits: Reduce landfill waste, support a circular economy, and are particularly suitable for pet waste disposal, food packaging, and municipal waste sorting. Low-quality bags may release microplastics during composting, causing secondary pollution.
- Common Uses: Retail shopping bags, poop bags for pet supply chains, FBA packaging for online sellers, dog walker collection by pet service companies, hotel room trash bags, and municipal organic waste collection.

Why Is the Quality of Compostable Bags Important?
Environmental Protection and Regulatory Compliance
- High-quality compostable bags certified by international standards such as EN13432, ASTM D6400, and AS4736 are fully biodegradable in composting environments, preventing plastic residue from harming soil and water, truly contributing to sustainable development goals and complying with regulatory requirements.
- Low-quality products can contribute to microplastic pollution, violate environmental protection principles, and may even fail regulatory review and import inspections.
Functionality and Practical Applications
- High-quality compostable bags are tough, leak-proof, and heavy-duty, making them easy to package, transport, and use daily, effectively alleviating operational pressures in the supply chain.
- Low-quality bags are prone to rupture or leakage, leading to inconvenient waste disposal, increased customer complaints, and potential secondary pollution.
Brand Image and Market Trust
- Using substandard bags for eco-friendly brands can severely damage their corporate image and undermine consumer trust in their sustainability commitments.
- Poor physical properties of bags (such as odor and damage) can directly impact user experience and brand reputation.
Cost and Operational Efficiency
- High-quality bags may have slightly higher initial costs, but their durability and compliance can effectively reduce additional costs such as returns, replacements, and supply chain management.
- Low-quality bags often result in returns, fines, or logistics delays due to non-compliance, which in turn increases overall operating costs.
Industry and Policy Requirements
Globally, countries and regions are gradually introducing mandatory standards and import certification requirements to regulate the production and distribution of compostable bags, driving companies to upgrade towards higher quality.
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) authoritative document on the need for third-party certification of compostable plastic waste to ensure safe composting:
“Compostability must be certified by an independent third party. Because of similar biodegradability properties, compostable plastic waste can be composted together with bio-waste, contributing to the production of high-quality compost.” — UNEP’s technical guidance document, “Technical guidelines on the environmentally sound management of plastic wastes,”
A 2023 conference document released by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) also emphasized the need for a third-party certification and labeling system for plastic products to ensure their safety and environmental friendliness.(https://resolutions.unep.org/resolutions/uploads/eubp_23082023_b.pdf)
Compostable Bag Quality Standards and Laboratory Testing
International compostable bag standards evaluate multiple performance indicators:
- Chemical safety: strict limits on heavy metals and toxic substances
- Biodegradability: at least 90% conversion into CO₂, water, and biomass within a defined period
- Disintegration: physical breakdown into fragments smaller than 2 mm
- Ecotoxicity: compost residue must be safe for plants and soil organisms
Relevant test standards include:
- ASTM D6400
- EN 13432
- ISO 14855
- GB/T 19277
Laboratory testing provides definitive proof of compostability and compliance, while on-site tests are used only for preliminary screening.
Sample Screening Tests Buyers Can Perform Before Bulk Orders (Simple Steps)
1. Strength Stretch Test
- Pull the edges of the bag with both hands.
- A high-quality compostable bag will not tear immediately.
- The handles should not show cracks or splitting during stretching.
2. Leak-Proof Test
- Fill the bag with about half its capacity with water.
- Leave it undisturbed for 10 minutes.
- If there is no leakage from the bottom, the bag passes the test.
3. Heat Softening Test (Very Important)
- Place the bag in a 40–50°C (104–122°F) environment for 48 hours.
- PLA/PBAT materials will soften slightly — this is normal and expected.
- PE plastic bags will remain unchanged, indicating they are not truly compostable.
4.Odor Test
- A faint plant-based smell indicates a genuine compostable material.
- A strong chemical or plastic odor suggests the presence of petroleum-based additives.
Compostable Bag Manufacturer Quality Control Procedures
Reliable compostable bag manufacturers implement strict quality control throughout production, including:
- Raw material inspection and traceability
- Thickness uniformity checks
- Seam strength and leakage testing
- Random batch sampling for large orders
Consistent quality control is especially important for wholesalers, retailers, and brand owners purchasing large volumes.
Warning Signs of Fake or Low-Quality Compostable Bags
Buyers should be cautious of products with the following characteristics:
- No verifiable certification number
- Vague labels such as “eco-friendly” or “biodegradable” without standards
- Overly glossy or crisp plastic-like texture
- Strong chemical odor
- Prices significantly below market average
- No expiration date or production batch information
These are common indicators of PE-containing or falsely labeled products.

Compostable vs Biodegradable Bags: Key Quality Differences
| Aspect | Biodegradable Bags | Compostable Bags |
|---|---|---|
| Degradation | Uncontrolled, may leave residues | Fully breaks down under defined conditions |
| Residue | Possible microplastics | No toxic residue |
| Certification | Often unclear or missing | Strict third-party standards |
| Environmental Impact | Uncertain | Supports circular economy |
Compostable Bag Certifications & Quality Standards
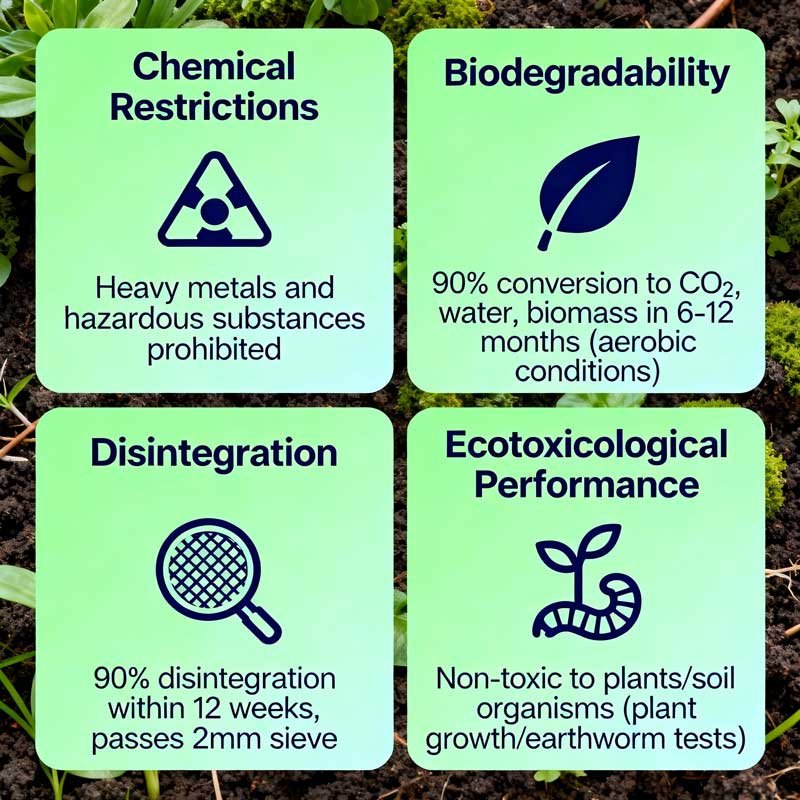
Evaluation Standards for Compostable Bags
The evaluation criteria for compostable bags are mainly based on the internationally recognized biodegradability and composting standard system, involving multi-dimensional indicators such as chemical safety, biodegradability, disintegration and ecotoxicology, to ensure that the bags can be safely and efficiently decomposed during the composting process without harming the environment.
Chemical Restrictions
Compostable bags must meet strict limits for heavy metals (such as lead, cadmium, and mercury) and fluorine, and must not contain any hazardous substances that could affect compost quality.
Biodegradability
The material must be microbially converted into at least 90% carbon dioxide, water, and biomass within a specified timeframe (6-12 months) under aerobic composting conditions. (Intertek Biodegradability Testing Services: https://www.intertek.com/biodegradability-testing/)
Disintegration
Within 12 weeks of composting, at least 90% of the material must be disintegrated and pass through a 2mm sieve, leaving no visible residue in the compost.
Ecotoxicological Performance
The composted product must be non-toxic to plants and soil organisms, including plant germination and growth, biomass survival testing, and earthworm toxicity testing.


Compostable Bag Quality Checklist
| Check Item | High Quality | Low Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Certification | BPI / EN13432 / AS5810 | No certificate number / Fake logo |
| Material | PLA + PBAT, plant-based, traceable composition | Contains PE, fake PLA |
| Feel | Soft, no crisp plastic sound | Smooth, strong plastic feeling |
| Odor | Light plant-based smell | Pungent or chemical odor |
| Thickness | Uniform 15–30 µm | Bubbles or weak spots |
| Strength | Can hold 5–10 kg | Easily torn |
| Leak-Proof | No leakage when filled with water | Seepage from bottom |
| Compost Test | Gradually becomes brittle and rough | No change for a long time |
How Importers Can Avoid Low-Quality Compostable Bag Suppliers
Importer Pre-Order Checklist
- Verify certificate numbers on official databases (BPI, DIN CERTCO, TÜV)
- Request recent laboratory test reports
- Inspect random samples for thickness, strength, and leakage
- Confirm export experience to regulated markets (US, EU, Australia)
In addition, buyers should conduct supplier audits, request production documentation, and test samples before bulk shipments.
Warning Signs of Fake or Low-Quality Compostable Bags
- Misleading Claims: Be wary of “biodegradable” labels without compost certification. These may simply be oxo-degradable products that break down into microplastics.
- Storage Issues: Bags can degrade prematurely in humid environments; check the expiration date and store in a cool, dry place.
- Supplier Reliability: Avoid small-scale suppliers and choose manufacturers with high-volume production capacity and global export experience to ensure a stable supply chain (especially for e-commerce sellers purchasing over 500 kg per month).
- Risks Customers Don’t Consider: Many people fail to consider regional standard differences. For example, Australian customers require AS5810 home composting certification, while the US prefers BPI. Our multi-certification portfolio covers these needs.

How to Identify Fake Compostable Bags
1. Check the Labels and Labels
Compostable bags typically have a special logo, such as the “jj” degradation symbol, a material abbreviation (such as PBAT or PLA), and the national standard number (such as GB/T 38082-2019) and degradation conditions.
Be cautious when purchasing bags without logos or simply labeled “environmentally friendly” or “degradable” without the standard number.
2.Touch the Material and Listen to the Sound
Authentic biodegradable bags have a soft, matte feel and no snapping sound when rubbed. Traditional plastic bags have a smooth feel and a crisp sound.
3.Smell the Odor
Biodegradable bags typically have a light plant-based starch aroma; inferior products may have a pungent fragrance or a plastic-like odor.
4.Scan the QR code to trace the source
Authentic products on the market often have a QR code that can be scanned to check the raw material ratio, test reports, and production information. If the code contains no information or does not match the information on the bag, it is likely counterfeit.
5.Simple home rapid test
Cut the bag into pieces and place it in 45°C warm water for three days. Genuine plastic bags will become rough and lose their toughness, while ordinary plastic bags will show no noticeable changes.
Use dichloromethane to test for swelling or dissolution, judging by chemical properties.
6.Check price and expiration date
Prices far below market norms or no expiration date indicate the bag is likely low-quality or counterfeit.
7.Fake Compostable Bags Warning Signs
Claims to be “100% biodegradable” but provides no certification number.
BPI or OK Compost logos cannot be verified on the official certification websites.
The material looks overly glossy or makes a crisp plastic sound, which usually indicates PE content.
Price is significantly lower than the market standard—for example, less than $0.50 per roll.
Labeled as “PLA,” but the material does not soften under heat and does not absorb moisture, indicating it is not truly compostable.

How Importers Can Avoid Low-Quality Suppliers
Require suppliers to provide authoritative certifications and test reports.
Certifications must include valid certificates and test reports from third-party organizations such as EN 13432 and ASTM D6400.
Site visits and supply chain audits
Understand the supplier’s production processes, raw material sources, and quality control procedures to ensure they have the expertise to produce compostable bags.
Sample testing
Laboratory testing of samples before import to verify degradation performance and safety indicators to avoid bulk purchases of substandard products.
Sign a quality assurance agreement
Clearly define product quality standards and liability for breach of contract to ensure suppliers assume responsibility for quality risks and safeguard purchasing rights.
Focus on market reputation and customer feedback
Choose reputable suppliers with industry certifications, and reference other customers’ experiences and reviews.
By combining label recognition, rapid testing, and supply chain audits, importers can effectively avoid purchasing counterfeit and low-quality compostable bags, ensuring product compliance and brand reputation.
FAQ
How do I know if packaging is really compostable?
Look for verifiable certifications such as ASTM D6400, EN 13432, or OK Compost, and confirm the certificate number on official databases.
How can you tell if a compostable bag contains PE?
Certification verification is the most reliable method. PE-containing bags often remain unchanged under heat and feel slick or overly plastic-like.
Are compostable bags strong enough for commercial use?
Yes. High-quality certified compostable bags can hold 5–10 kg and remain leak-proof when properly manufactured.
Are all compostable bags suitable for home composting?
No. Some bags are designed only for industrial composting. Look specifically for “home compostable” certification if required.
Conclusion
Checking compostable bag quality requires more than visual inspection. Importers and buyers must verify certifications, confirm material composition, review laboratory test reports, and evaluate supplier quality control.
Certified compostable bags are not just environmentally responsible—they reduce regulatory risk, improve operational efficiency, and protect brand reputation. By applying the methods in this guide, buyers can confidently source compliant, high-quality compostable bags and avoid costly mistakes.




