BPI Certification: Meaning, Standards & How to Verify
Table of Contents
This page is for certification reference and compliance education.
The form below is for B2B verification and documentation requests only (e.g., certificate files, database verification, compliance statements). Retail and personal requests will not be processed.
BPI Certification is a third-party compostability certification used in the United States and Canada.
It confirms that finished products meet ASTM D6400 or ASTM D6868 standards and are designed to break down in industrial composting facilities.
Quick Answer
BPI Certification is a third-party compostability certification used in the United States and Canada to verify that finished products meet ASTM D6400 or ASTM D6868 standards for industrial composting.
What does “BPI compostable” mean?
It means the finished product is certified and listed in the official BPI database.Is BPI home compostable?
No. BPI applies only to industrial composting systems.How do I verify a BPI certified product?
Search the product or company in the BPI certified products database.
When you see “BPI Certified Compostable,” it means the finished product is certified to meet ASTM D6400 or ASTM D6868 and is intended for industrial composting programs in the U.S. and Canada. This page explains what the certification means, how to verify it, and how to use it correctly.

What Is BPI Certification?
BPI Certification is a third-party program run by the Biodegradable Products Institute. BPI checks whether a product can safely break down in commercial compost systems. Certified products such as commercial compostable trash bags are widely accepted by industrial composting facilities across the United States. These systems operate at high temperatures and have controlled airflow and moisture. They are very different from a backyard compost bin.
To become BPI certified, a product must meet the rules of:
-
ASTM D6400 – compostable plastics
-
ASTM D6868 – compostable coatings, paper liners, and packaging
BPI also checks the product’s ingredients and reviews its labeling. When a product passes all steps, it earns the BPI Certified Compostable Mark. Composting facilities in the U.S. use this mark as a trusted signal. https://bpiworld.org/Certification
What Does “BPI Compostable” Mean?
“BPI compostable” means the finished product is certified by the Biodegradable Products Institute and listed in the official BPI database for industrial composting.
Official references:
- BPI certification overview: https://bpiworld.org/Certification
- BPI products database: https://bpiworld.org/products
- BPI logo guidelines: https://bpiworld.org/Logo-Guidelines
“BPI compostable” means the finished product (not only the resin) has passed ASTM compostability tests and is approved by BPI for industrial composting programs in North America.
It does NOT mean the item will break down in landfills, oceans, or every backyard compost bin.
If you are buying compostable bags for a municipal or food waste program, this label is often the fastest way to reduce contamination risk.
Many programs also follow strict sorting rules, so it helps to understand BPI certified compostable products within real composting streams.
If you are unfamiliar with the term, this guide explains what does BPI compostable mean and how certification applies to finished products.
Standards Behind BPI Certification (ASTM D6400 & ASTM D6868)
These two standards are the backbone of the BPI program. They are technical documents, but I can summarize them simply.
ASTM D6400
This standard applies to compostable plastics. It measures how fast the plastic biodegrades, how well it breaks apart, and whether it harms the finished compost.
ASTM D6868
This standard applies to items made of paper or fiber that include a compostable coating or film. It makes sure the coating also meets composting rules.
Together, they provide clear criteria for industrial compostable certification in North America.

Key Requirements for BPI Certification
For a product to earn the BPI certified compostable label, it must pass several scientific tests. These tests are done by independent labs.
1. Biodegradation
The material must convert into carbon dioxide, water, and biomass. It cannot remain as microplastic. This process must follow the curve defined in ASTM D6400.
2. Disintegration (84 Days / 12 Weeks)
In a commercial composting system, the item must break into small fragments. After 12 weeks, no large pieces should remain. This is important for compost quality.
3. Ecotoxicity and Plant Safety
The finished compost must support healthy plant growth. It must not introduce harmful chemicals or toxic byproducts into the soil.
4. Heavy Metals and Hazardous Substances
BPI enforces limits on metals like lead, cadmium, and mercury.
In recent years, BPI also added rules that restrict PFAS and other chemicals found to be harmful in composting systems (source: BPI policy update, 2023–2024).
5. Ingredient Review and Labeling
BPI reviews every additive, coating, and ink used in the product. The label must follow BPI’s style guide so composters can quickly identify certified items.
These requirements make BPI one of the most reliable industrial compostability certifications in North America.
Why BPI Certification Matters for Businesses
Your customers, waste haulers, and composting facilities need clear and honest labeling. BPI certification helps solve several real-world problems:
Avoiding greenwashing
Many products claim to be “biodegradable.” Without testing, this claim is unreliable.If you’re unsure why “biodegradable” claims often fail compliance, start with this simple guide on BPI certification and the compostable standards behind it.Accepted by composting facilities
Many U.S. municipal programs only accept BPI certified compostable bags and packaging.Meeting retailer and food service requirements
Large food chains and supermarkets often require suppliers to use certified compostable packaging in their organics programs.Supporting sustainability goals
Certified products help move food scraps and compostable packaging away from landfills and into industrial compost systems.
For companies selling compostable bags, liners, and packaging, BPI certification is not a bonus. It is essential.
Composting facilities rely on BPI certification because it helps them keep contamination low and maintain high-quality compost. Clear labeling reduces sorting problems and prevents non-compostable plastics from entering the system.
When you see a product marked with BPI Certified Compostable, it means something very specific.
The product has been tested under strict rules to confirm it can break down in an industrial composting facility.
As someone who works with compostable materials every day, I want to explain what this certification really means and how you can use it with confidence.
For procurement teams, the biggest risk is not performance—it’s compliance and acceptance. Choosing certified products helps reduce labeling disputes and contamination issues in organics streams. If you source packaging for distribution programs, you can also review our guide to certified compostable bags for North America.
BPI Certification vs Other Compostability Standards
BPI certification is mainly used for industrial composting programs in the U.S. and Canada. If you sell into other regions, you may also need additional compostability standards—such as EN 13432 for the EU, AS4736 for Australia industrial composting, or OK Compost HOME/INDUSTRIAL for specific labeling and acceptance requirements.
Here is a simple comparison to help you understand where BPI fits among global certifications:
| Standard | Region | Compost Type | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPI Certification | USA & Canada | Industrial composting | North America market |
| EN 13432 | Europe | Industrial composting | EU export |
| OK Home Compost | Global | Home composting | Light packaging |
| AS4736 / AS5810 | Australia | Industrial / Home | AU / NZ organics programs |
Each certification is designed for a specific region and compost system.
If you sell globally, you may need more than one certification.
Our BPI Certified Products
We offer a range of BPI certified compostable bags for professional organics collection and food waste programs. All products listed below are finished-product certified and can be verified in the official BPI database.
Below you can see the BPI certified compostable products we currently offer. Each listing includes the material type and certificate number. I believe transparency is important, so you can check these certificates directly.
If you need the full test report or logo authorization files, I can provide those upon request.
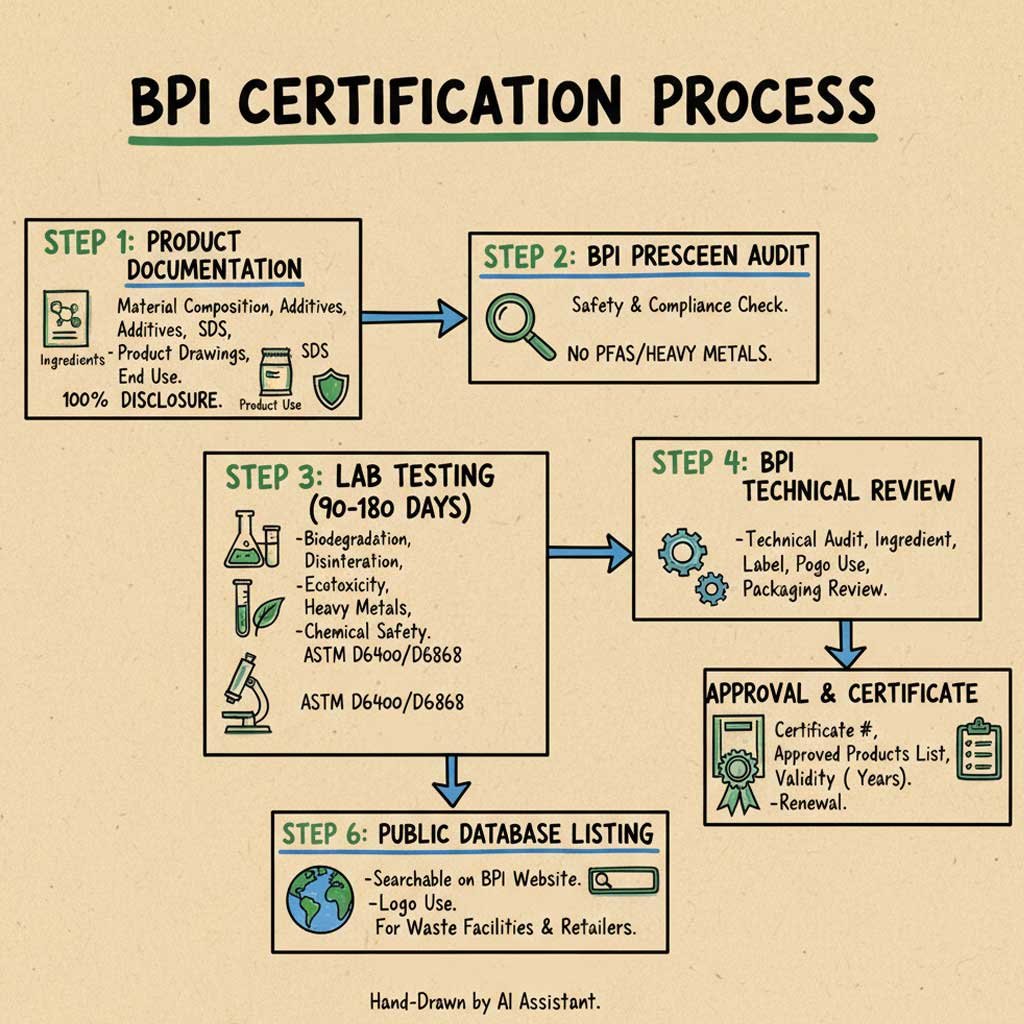
How to Apply for BPI Certification (Step-by-Step Guide)
BPI certification relies on recognized ASTM test methods, including the ASTM D6400 compostable standard, to evaluate industrially compostable plastic products.
Getting a product certified by BPI involves several scientific evaluations and documentation checks.
Here is the complete application process:
Step 1 — Prepare Product Documentation
You must provide:
- Full material composition (PLA/PBAT/Starch ratios)
- Additive, colorant, and ink disclosures
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
- Product drawings / film structure
- Intended end-use (bags, liners, packaging, mailers, etc.)
BPI requires 100% ingredient transparency before testing begins.
Step 2 — Pre-Screening Review by BPI
BPI reviews material safety and ingredient compliance.
If any chemical exceeds limits (such as PFAS, heavy metals), the product cannot enter certification testing.
Step 3 — Laboratory Testing (ASTM D6400 or D6868)
Testing must be conducted by a BPI-approved independent laboratory, which evaluates:
- Biodegradation curve
- Disintegration (84-day breakdown test)
- Ecotoxicity (plant growth test)
- Heavy metal limits
- Chemical safety
Testing typically takes 90–180 days depending on the product.
Step 4 — BPI Technical Review
After the lab submits test data, BPI performs:
- A technical audit
- Ingredient review
- Labeling review
- Packaging inspection
Step 5 — Approval & Certificate Issuance
When all requirements are met, BPI issues:
- Certificate Number
- Approved Products List
- Logo Usage Authorization
- Validity Period Information
Products must be renewed every 3 years, or earlier if the formula changes.
Step 6 — Listing on the BPI Public Database
Once approved, the product becomes publicly searchable on the BPI official website — a key requirement for waste facilities and retailers.
How to Verify a BPI Certified Product
Online and on Reddit, I notice many people confused by labels. Some products look “green,” but they are not certified. Here is a clear way to check:
1. Search the BPI Official Database
Go to BPI’s website and type the product name or company name.
If it is not listed, it is not certified.
2. Check the Certificate Number
A real BPI certified compostable product will include a valid certificate number. This number should match the database entry.
3. Look for the Correct BPI Logo
The logo must match BPI’s approved format. If it looks altered or incomplete, treat it as a red flag.
4. Know the Difference: Resin Certification vs Product Certification
Sometimes a raw material resin is certified, but the finished product is not.
A bag, cup, or film must be certified as a final item, not only by material.
5. Watch for Greenwashing
Claims like “earth-friendly,” “oxo-biodegradable,” or “biodegradable plastic” do not guarantee compostability.
By following these steps, you can avoid false claims and choose trustworthy compostable packaging.
You can verify any certified item through the official BPI Product Database:
https://bpiworld.org/products
BPI Certification Cost Breakdown
How Much Does BPI Certification Cost?
The total cost of BPI certification depends on product type, testing requirements, and company size.
Generally, manufacturers should expect:
| Cost Item | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| ASTM testing (D6400 / D6868) | USD 6,000 – 12,000 per product |
| Ingredient screening fees | USD 300 – 1,000 |
| BPI application fee | USD 500 – 1,500 |
| Annual licensing fee | USD 2,000 – 4,000 per year |
| Logo usage fee | Included in annual fee |
| Re-certification (every 3 years) | Similar to original application |
Factors affecting cost
Thickness of product
Multi-layer structure
Number of SKUs
Extremely large or extremely small items
Use of specialty inks or coatings
For brands, BPI certification ensures compliance with waste programs.
For manufacturers, certification helps you enter the North American compostable packaging market.

Correct Disposal of BPI Certified Products
A BPI certified product is meant for industrial composting, not a backyard compost pile. The temperatures in home compost are usually too low to meet ASTM conditions.
To dispose of certified items correctly:
Place them in your local organics or food waste bin
Check whether your city accepts compostable packaging
Do not put them in recycling bins
Do not send them to landfill unless you have no composting option
Using the right bin keeps compost free from contamination and protects the composting system.
For organics collection programs, many buyers choose BPI certified compostable bags designed for clean sorting and stable performance.
Where Is BPI Certification Required or Recommended?
United States
Many state and municipal composting programs accept only BPI-certified products.
| Region | Regulation | Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| California (SB 270 / SB 1383) | Strict composting rules | BPI-certified bags strongly recommended |
| Washington State | Compostable labeling law | BPI certification recognized |
| Colorado | Organics recycling expansion | Programs prefer BPI-certified bags |
| Oregon | Food waste programs | Many facilities require certified liners |
| New York City | Commercial composting | Certified compostable bags required |
Canada
Cities such as Vancouver, Toronto, Calgary prefer BPI-certified compostable liners for organics collection.
Why Regulations Matter
Reduces contamination in compost systems
Ensures packaging meets safety standards
Helps waste haulers easily identify “true compostables”
Required by many supermarkets and food chains

Industries That Commonly Require or Prefer BPI Certified Compostable Packaging
1. Supermarkets & Grocery Chains
For collecting food scraps and organic waste.
Brands like Whole Foods use certified bags to meet sustainability goals.
2. Food Service Providers
Restaurants, cafes, meal-prep kitchens, and corporate cafeterias.
3. Waste Haulers & Composting Facilities
Many municipal facilities require BPI-certified liners to reduce contamination.
4. Retailers & Zero-Waste Stores
To ensure packaging claims are legitimate and auditable.
5. Commercial Kitchens
Certified liners ensure safe disposal of organic waste.
6. Event Organizers (Zero-Waste Events)
Certified products prevent contamination during large events.
7. Healthcare & Institutional Facilities
Used in organic waste and compostable paper collection programs.
Why Products Fail BPI Certification
Even well-designed compostable products may fail testing due to:
1. Materials that do not biodegrade fast enough
Example:
- PBAT ratio too high
- PLA crystallinity causing slow biodegradation
2. Excessive thickness
If the bag is too thick, it may not disintegrate within 84 days.
3. Toxicity or chemical safety issues
Including:
- Heavy metals above limits
- Non-compliant inks or pigment
- Additives failing plant growth tests
4. Incorrect or incomplete documentation
This is one of the most common reasons manufacturers fail.
5. Misuse of the BPI logo
If labeling violates guidelines, certification can be suspended.
6. Resin certified ≠ finished product certified
Many companies misunderstand this rule.
Certified Compostable Bags vs Non-Certified Bags
| Feature | BPI Certified | Non-Certified |
|---|---|---|
| Tested under ASTM D6400 / D6868 | ✔ | ❌ |
| Validated by independent lab | ✔ | ❌ |
| Ingredient transparency | ✔ Required | ❌ |
| Accepted by composting facilities | ✔ | ❌ Often rejected |
| Complies with state regulations | ✔ | ❌ |
| Risk of greenwashing | Minimal | Very high |
Business Risks of Using Non-Certified Bags
- Waste haulers may reject your packaging
- Composters may charge contamination fees
- Retailers may remove products that violate sustainability claims
- Violates labeling laws in states such as California and Washington
- Potential PR and ESG compliance risks
Why BPI Certification Protects Your Brand
- Clear scientific proof
- Transparent ingredients
- Reduced risk of greenwashing claims
- Higher acceptance across U.S. composting programs

BPI Logo & Labeling Rules
The BPI logo is more than a symbol. It helps composting facilities sort materials correctly. https://bpiworld.org/Logo-Guidelines
A product using the BPI logo must:
Display the logo clearly
Use the correct shape and wording
Apply it only to items covered by the certificate
Avoid misleading references like “BPI approved” when only the resin is certified
Misusing the logo may lead to certification removal.
Clear labeling keeps compost clean and helps facilities trust your materials.
Download BPI Certificates
You can download our certification files below:
- BPI Certificate (PDF)
- Test Result Summary
- Ingredient Disclosure
- BPI Logo Use Guide
If you need documentation for compliance checks or supplier verification, feel free to contact me.
FAQ About BPI Certification
Is BPI the same as ASTM D6400?
Not exactly. ASTM is a testing standard. BPI is a third-party certification that verifies products meet those standards.
Does BPI mean industrial compostable?
Yes. BPI certification applies only to industrial composting, not home compost systems.
How do I check if something is BPI certified?
Search the product name on the BPI website or review its certificate number.
Does BPI cover the final product or just the material?
BPI certifies the finished product. Resin alone is not enough.
Do composting facilities require BPI certification?
Many U.S. programs do. It helps them avoid contamination and maintain compost quality.
Learn More About “BPI Compostable” Meaning
If you want a simple explanation of what “BPI compostable” means in everyday use, you can read our full article that explains the term, real examples, and how compostable materials behave in different systems.
If you need BPI certified packaging or want to verify a specific product, you can contact me and I will provide all certificate files and material details.
This page is not about composting theory or marketing claims.
It focuses on real certification, backed by testing standards such as ASTM D6400 and ASTM D6868, which the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) uses to approve compostable products in the United States and Canada.
